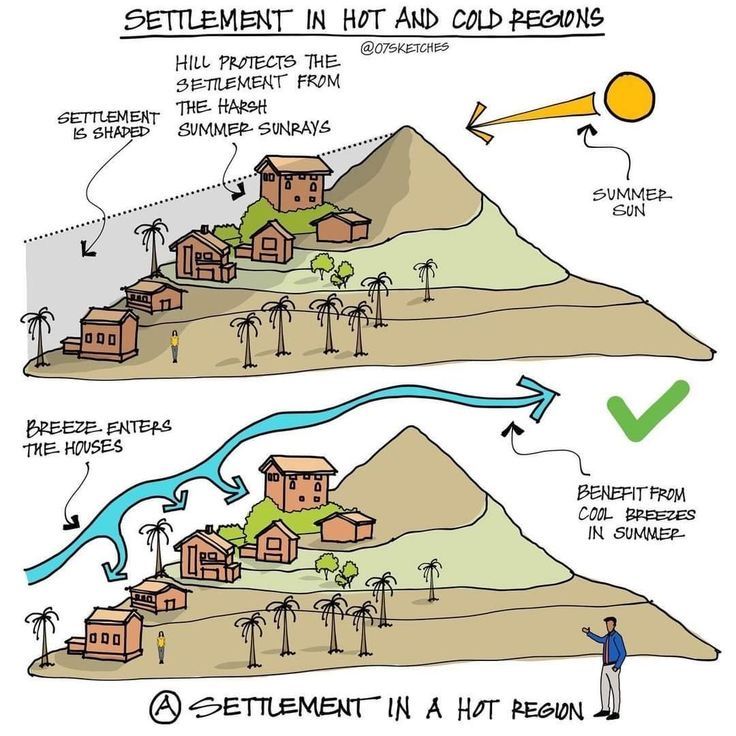
Smart settlement planning uses hills and breezes to shield homes from scorching sun and ensure cooler living conditions.
☀️ Living With Heat: A Challenge for Settlements
In many parts of the world, communities live in regions where summers are long, hot, and harsh. Rising global temperatures are making this challenge even more severe. For centuries, people have looked for natural ways to adapt to heat, and one of the smartest solutions has been to design settlements that work with the landscape instead of against it.
This diagram beautifully illustrates how settlements in hot regions can be shaped to provide maximum comfort: by using hills as shields from the blazing sun and orienting houses to catch cooling breezes.
🌄 Hills as Natural Shields Against the Sun
One of the most brilliant aspects of traditional settlement design is the use of topography as a natural protector.
- How it works:
When houses are built on the slope of a hill that faces away from the harshest rays of the summer sun, the hill itself blocks much of the direct heat. This keeps the settlement cooler without the need for artificial cooling systems. - Benefits:
- Lower Temperatures Indoors – Less sunlight directly hitting homes means less heat absorbed.
- Energy Efficiency – Families rely less on cooling devices like fans or air conditioners.
- Health Protection – Reduces heatstroke risks during extreme summers.
This clever placement turns a simple hill into a giant natural umbrella.
🌬️ Catching the Cool Breezes
Heat isn’t just about sunlight — air circulation is equally important. Settlements in hot regions often take advantage of prevailing winds.
- How it works:
By positioning homes to face the direction of natural breezes, cool air flows directly inside. Streets and pathways are also aligned to act like channels, guiding breezes deeper into the settlement. - Benefits:
- Comfortable Interiors – Natural airflow cools homes even during peak heat.
- Reduced Humidity – Breezes prevent the air from becoming stale and sticky.
- Outdoor Livability – Courtyards and shaded spaces remain usable throughout the day.
In short, breeze orientation is like free air conditioning provided by nature.
🏘️ The Shape of Settlements
The diagram also shows that settlements are shaped carefully in hot regions:
- Compact Clusters → Houses are placed close together, reducing the amount of direct sunlight hitting walls and creating shaded streets.
- Staggered Levels → Building at different heights ensures airflow is not blocked.
- Natural Vegetation → Trees are often planted around homes for extra shade and evapotranspiration cooling.
This thoughtful layout is not random — it’s centuries of wisdom in climate-adaptive architecture.
🌍 Lessons From Traditional Settlements
Many ancient civilizations perfected these strategies:
- Middle Eastern towns often had narrow streets aligned with wind corridors.
- Indian desert settlements like Jaisalmer used dense housing clusters and sandstone walls to reduce heat.
- Mediterranean hillside villages used terrain for shading and cool airflow.
These traditional designs remind us that nature-inspired solutions are timeless and often more effective than expensive modern fixes.
🔥 Why This Matters More Than Ever
With climate change, heatwaves are becoming more frequent and intense. Poorly designed modern settlements — with wide asphalt roads, minimal vegetation, and houses exposed to direct sun — trap heat and worsen urban living. This is known as the Urban Heat Island Effect.
By contrast, hillside protection and breeze-friendly design offer:
- Sustainability – Reduced energy use for cooling.
- Affordability – Less dependence on costly infrastructure.
- Resilience – Homes stay livable even during power outages.
This is not just about tradition; it’s about future-proofing communities.
🏗️ Modern Applications
Urban planners and architects are beginning to revive these principles:
- Eco-Housing Projects → Using natural terrain and wind patterns to reduce reliance on air conditioning.
- Green Roofs & Walls → Adding vegetation to mimic natural shading.
- Passive Cooling Systems → Designing windows and openings to maximize breeze entry.
These approaches prove that settlements of tomorrow can learn from the past.
✅ The Takeaway
This image offers a clear lesson:
- In hot regions, settlements should be protected from direct sun and open to cooling breezes.
- Hills are not obstacles — they’re natural shields.
- Airflow is not random — it can be guided and used strategically.
By respecting these natural forces, settlements can become cooler, healthier, and more sustainable.
As the world grows hotter, these timeless design principles will play a vital role in ensuring human comfort and survival. 🌿
✨ Final Words
The beauty of hillside settlement planning lies in its simplicity. It doesn’t require advanced technology or massive budgets. It requires understanding the land, the sun, and the wind.
This is architecture that respects nature and uses it as an ally. If modern planners take this wisdom seriously, we could see a future where even the hottest regions of the world remain comfortable — not by fighting nature, but by living in harmony with it.