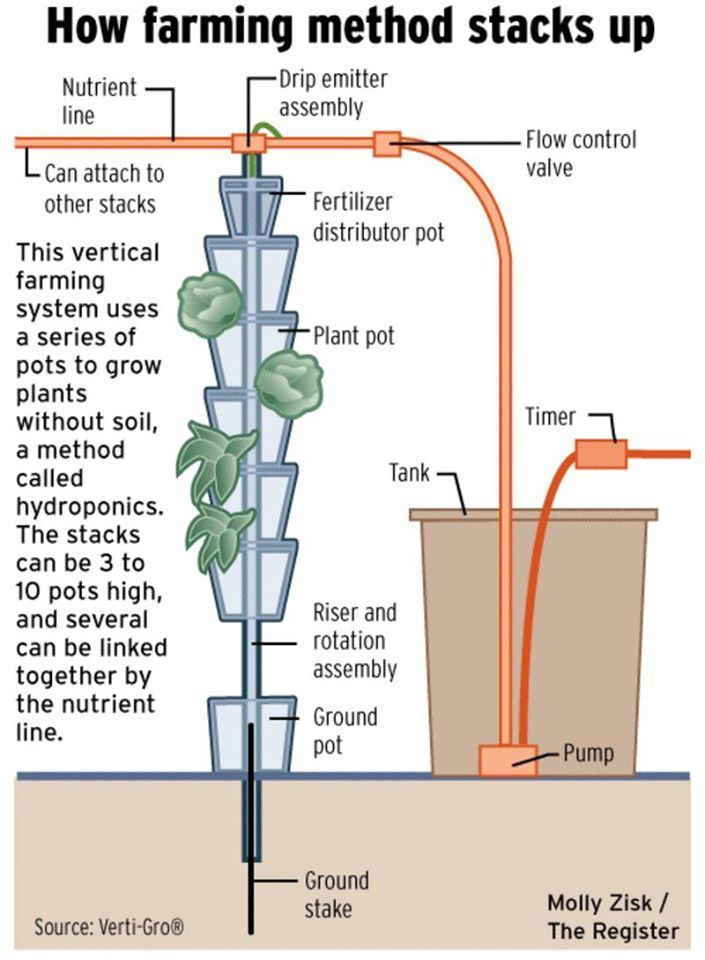
“A soil-free, space-saving method uses nutrient-rich water and stacked pots to grow more food with less land.”
🔹 How the System Works
- Tank & Pump
- Everything begins in a water tank filled with nutrient-rich solution.
- A pump pushes this liquid upward into the system.
- Flow Control & Timer
- A flow control valve regulates how much nutrient water goes to the plants.
- A timer automates irrigation, ensuring plants get the right amount of water and nutrients without waste.
- Nutrient Line & Drip Emitters
- The water travels through a nutrient line and reaches drip emitter assemblies at the top.
- These emitters evenly distribute the solution into the pots.
- Fertilizer Distributor Pot
- At the top of the stack, a fertilizer distributor pot spreads the nutrient solution downward.
- Gravity helps the liquid flow from one pot to another, feeding all plants along the stack.
- Stacked Plant Pots
- The system is built with multiple plant pots stacked vertically—usually 3 to 10 pots high.
- Each pot grows crops like lettuce, herbs, or strawberries, all without soil.
- Several stacks can be connected together using the same nutrient line.
- Riser & Ground Support
- A riser and rotation assembly keeps the stack upright.
- A ground pot at the base supports the system, anchored by a ground stake for stability.
🔹 Why This Farming Method Matters
✅ Soil-Free Cultivation – Uses hydroponics, where water delivers nutrients directly to roots.
✅ Space-Saving Design – Ideal for urban areas, rooftops, and small farms.
✅ Water Efficient – Uses up to 90% less water than traditional farming.
✅ Scalable – Systems can be linked together, making it suitable for both home gardening and commercial farming.
✅ High Yield – Vertical design allows more crops to be grown in less space.
🔹 Real-World Impact
- Urban Agriculture: Cities with limited land can grow food on balconies, rooftops, and indoors.
- Sustainability: Reduces the need for pesticides and soil management.
- Food Security: Helps communities grow fresh vegetables locally, reducing transport costs and emissions.
👉 In simple terms: Instead of planting crops across wide farmland, we’re now growing them upward in stacks! 🚀